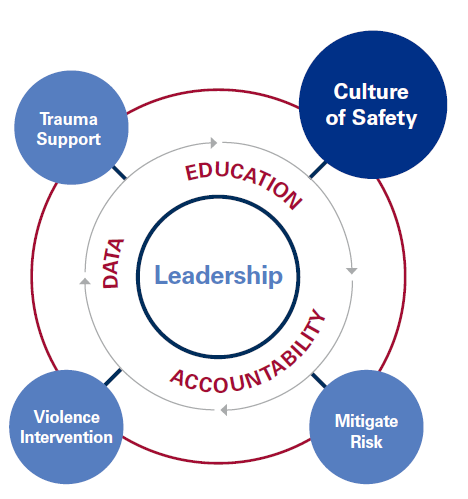
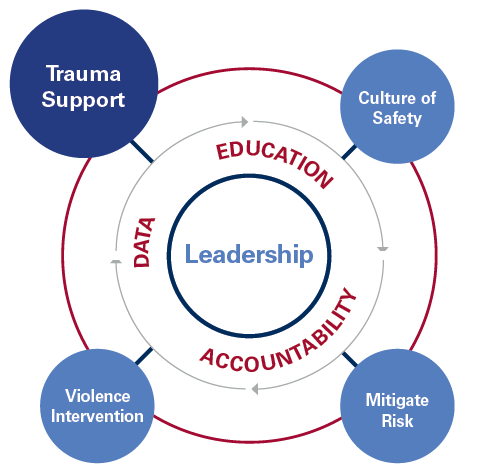
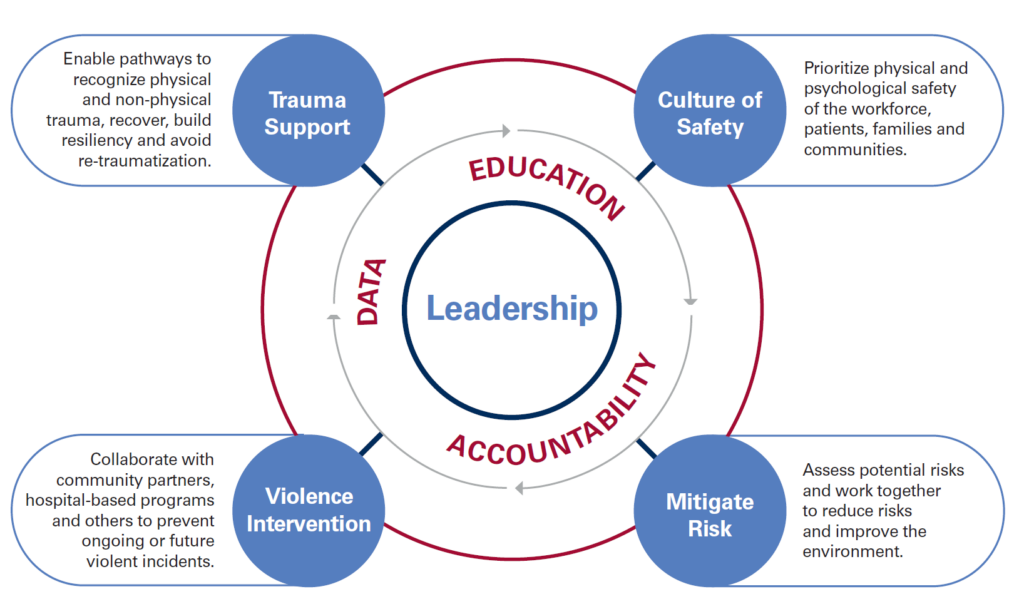
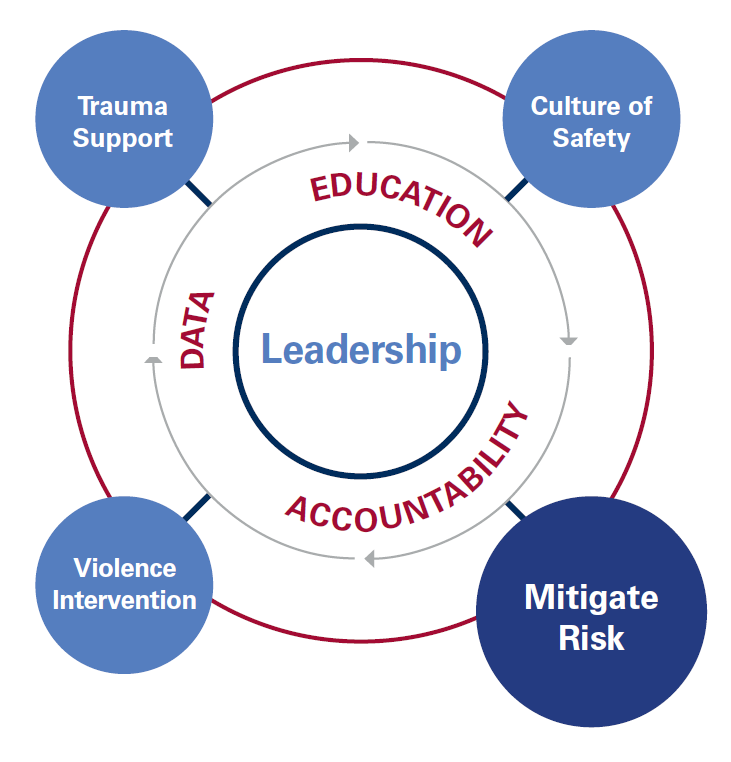
In response to the increased risk of violence in healthcare settings, the Massachusetts Health & Hospital Association’s Healthcare Safety and Violence Prevention Workgroup (HSVPW) developed guidance to help healthcare facilities use evidence-based practices to create effective healthcare violence prevention programs.
Six years after the initial guidance was released, MHA consulted with the workgroup to produce an updated version: Guidelines for Healthcare Safety & Violence Prevention. The updated guidance provides additional strategies that have emerged over the past few years to support member organizations with maintaining a safety culture, reducing risk of violence, and improving wellbeing and outcomes for patients, visitors, providers, and staff.
This update offers newly revised strategies for a comprehensive approach to healthcare safety and violence prevention across healthcare facilities, including emergency departments, inpatient settings, outpatient clinics, mobile health services, and home healthcare. It also recognizes that because every healthcare organization has its own unique needs, structures, economics, patient populations, and workforce environments, each entity’s response to workplace violence will be different. There is no one single way to implement a workplace violence strategy for a healthcare setting, but these collected strategies can assist.
Over the last few years, the HSVP’s accomplishments include adopting and reporting on a standardized data collection tool, creating a united set of principles for patient-visitor codes of conduct, providing regular education opportunities to disseminate safety and violence prevention strategies from local and national leaders, and advocating for federal and statewide policy changes related to healthcare worker protections. Taken together, these efforts have helped make Massachusetts a recognized national leader in healthcare safety and violence prevention and prompted collaboration and publications with colleagues across the country.