The DAA is Where people come together to exchange ideas, form friendhsips and professional connections, and change lives to create a getter workd in which to live with dementia.
Author: admin
Dementia Friendly Massachusetts
Dementia Friendly Massachusetts is a grassroots movement to make communities safe, inclusive and respectful for persons with Alzheimer’s disease, or a related dementia.
Dementia Friendly Massachusetts is a grassroots movement to make our state “dementia friendly.” In dementia friendly communities, people with dementia feel safe and supported. There are many ways you can help.
AHRQ’s Effective Health Care Program – Interventions – Dementia Executive Summary
Interventions To Prevent Age-Related Cognitive Decline, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Clinical Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia – Executive Summary
Key Messages:
- Most interventions showed no evidence of benefit to delay or prevent age-related cognitive decline, MCI, and/or CATD.
- Some forms of cognitive training improve the performance of the specific target of training for adults with normal cognition, but little evidence supports transfer of benefits to other cognitive areas or reduced dementia incidence. Benefit for any form of cognitive training beyond 2 years is less certain.
- Some types of physical activity, and vitamin B12 plus folic acid, may benefit cognitive performance in some areas.
HRET Culture of Safety Top Ten Checklist
This Culture of Safety Top Ten Checklist includes steps to review current interventions or initiate new ones to ensure a culture of safety in your facility.
MHQP’s Adult Preventive Care Guidelines
About the MHQP Adult Preventive Care Guidelines
MHQP’s 2018 guidelines were developed by a collaborative group of Massachusetts healthcare organizations. These are recommendations for providing preventive care to adult patients from the general population. These guidelines should not supplant clinical judgment or the needs of individual patients. These guidelines are intended as quality-practice recommendations and are not intended as a description of benefits, conditions of payment, or any other legal requirements of any particular health plan or payor. Each health plan or payor makes its own determination of coverage and benefits. In the event that these practice recommendations are inconsistent with any applicable laws or regulations, such laws or regulations take precedence.
HRET Culture of Safety Change Package
This change package is a summary of themes from the successful practices of high performing health organizations across the country. It was developed through clinical practice sharing, organization site visits and subject matter expert contributions. This change package includes a menu of strategies, change concepts and specific actionable items that any hospital can choose to implement based on need or for purposes of improving patient quality of life and care. This change package is intended to be complementary to literature reviews and other evidence-based tools and resources.
Dementia Friendly Massachusetts Initiative – Statement of Values
As more individuals and organizations recognize the need to make our communities work better for the growing number of people living with Alzheimer’s or a related disorder, and their families and friends (“care partners”), it is helpful to define what it means to work toward becoming a “dementia-friendly” community.
ALZConnected – A Place to Share Concerns & Get Advice
ALZConnected® , powered by the Alzheimer’s Association®, is a free online community for everyone affected by Alzheimer’s or another dementia, including:
- People with the disease
- Caregivers
- Family members
- Friends
- Individuals who have lost someone to Alzheimer’s
What is the Cycle of Violence?
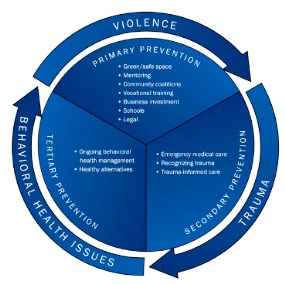 According to the AHA/ACHI Hospital Approaches to Interrupt the Cycle of Violence guide, exposure to violence significantly increases the likelihood of an individual being a perpetrator of violence or experiencing repeated violent injury in the future, creating an ongoing cycle of violence.
According to the AHA/ACHI Hospital Approaches to Interrupt the Cycle of Violence guide, exposure to violence significantly increases the likelihood of an individual being a perpetrator of violence or experiencing repeated violent injury in the future, creating an ongoing cycle of violence.
Prevention poses a challenge because violence occurs as part of a cycle of learned behaviors that are further perpetuated by an individual’s exposure to trauma. Though it may appear to be an intractable problem, violence can be prevented by addressing the underlying socioeconomic, environmental and behavioral risk factors that increase the likelihood that an individual will become a victim or perpetrator of violence.
Hospitals can play an important role at each level of prevention. By partnering with community stakeholders, hospitals can implement primary prevention approaches to address risk factors at the relationship, community and society levels and help prevent violence from occurring.
Through the Eyes of the Workforce: Creating Joy, Meaning, & Safer Health Care
Workplace safety is inextricably linked to patient safety. Unless caregivers are given the protection, respect, and support they need, they are more likely to make errors, fail to follow safe practices, and not work well in teams. A new report from the Lucian Leape Institute looks at the current state of health care as a workplace, highlights vulnerabilities common in health care organizations, discusses the costs of inaction, and outlines what a healthy and safe workplace would look like. The report concludes with seven recommendations for actions that organizations need to pursue to effect real change.









